- The word vitamin was first used by Polish biochemist Casimir Funk in 1912.
- The word vitamin was first used by Polish biochemist Casimir Funk in 1912.
- ‘Vita’:‘Life’
 -Europeans who established colonies in Asia in the 1800s brought rice polishing machines with them. Local people, whose main food source is rice, are encouraged to consume rice that has been removed from its shell and outer surface, and Beriberi, which is accompanied by neurological findings, begins to be common.
-Europeans who established colonies in Asia in the 1800s brought rice polishing machines with them. Local people, whose main food source is rice, are encouraged to consume rice that has been removed from its shell and outer surface, and Beriberi, which is accompanied by neurological findings, begins to be common.
-Beriberi becomes an epidemic in the Dutch colony, where Indonesia is now located, and Dr. Christian Eijkman writes an article about Beriberi being an infectious disease.
-Dr. from the Japanese Navy. Kanehiro Takaki reveals a connection between diet and Beriberi disease in sailors. When white rice is replaced by barley, vegetables, fish and meat, a regression in the disease is observed.
-In 1906, Frederick Hopkins said that foods contain carbohydrates, fat, protein and minerals, as well as a number of accessory factors necessary for health.
-In 1912, Polish chemist Casimir Funk claimed to have detected an "anti beriberi factor" in his studies and named it "vital amine". In 1926, the presence of a substance in rice husk that prevents beriberi was revealed. The 1929 Physiology or Medicine Award was given to Hopkins and Eijkman for their work.
Why do vitamin deficiencies develop?
Adults;
-Inadequencies in nutrition awareness and education, inability to access food, inadequate intake of vitamin-rich foods and not consuming balanced amounts
-Nutrient losses that take place during food production, cooking, packaging, transportation and storing.
-Presence of factors that inhibit absorption and synthesis
Medications (E.g. Metformin- B12 malabsorption)
Alcohol
Avoiding contact with the sun
-Conditions that cause malabsorbtion,
Advanced age
B12 malabsorption due to IF deficiency in the stomach (Atrophic Gastritis, Pernicious Anemia)
Bariatric Surgery, Ileum resection
H pylori Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Celiac
Parasitosis…
-Long-term drug use Proton pump inhibitors
Antacids,
Antibiotics,
Oral contraceptive use,
Metformin,
Anticonvulsant drugs
-In chronic malabsorption
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Celiac Disease
Diabetes Mellitus
-Chronic Liver Failure
-In Chronic Kidney Failure
Who may develop vitamin deficiency?
-Those who cannot receive adequate and balanced nutrition (millions of people living on the border of hunger and poverty)
-Old age patient
-Patient who underwent bariatric surgery, ileal resection
-Vegetarians (especially no animal foods) vegans who do not consume)
-Increased need for vitamin D in infants and children
-Pregnancy and lactation period
-Increased Vitamin D requirement after menopause
-Vitamin D deficiency in a patient who does not see the sun
-Oral contraseptive use, increases the need for Vitamin B6, B12 and minerals like zinc and folic acid
-Corticosteroid use increases the need for vitamin D and calcium.
Reasons for vitamin deficiency in infants and preschool children;
-Insufficient vitamin intake and storage of the mother pre and during the pregnancy,
-Babies’ not feeding purely on mothers milk in the first six months period,
-Not starting appropriate complementary food after six months period ,
-Not continuing breastfeeding up to 2 years of age with complementary food,
-Insufficient quality and quantity of the complementary foods,
-Failure to comply with protective principles while preparing, cooking and storing foods
-Enzymatic and chemical reactions that may be caused by yeast, mold and bacteria in the structure of the food may cause deterioration and change in the structure of the food.
-During consumption, all vitamins, especially Vitamin C and B group vitamins, lose their effectiveness as they are exposed to heat, light and alkali at different rates. Loss of up to 90-95% of Folic Acid can be expected as a result of exposure to heat.
Is the nutritional value of food decreasing?
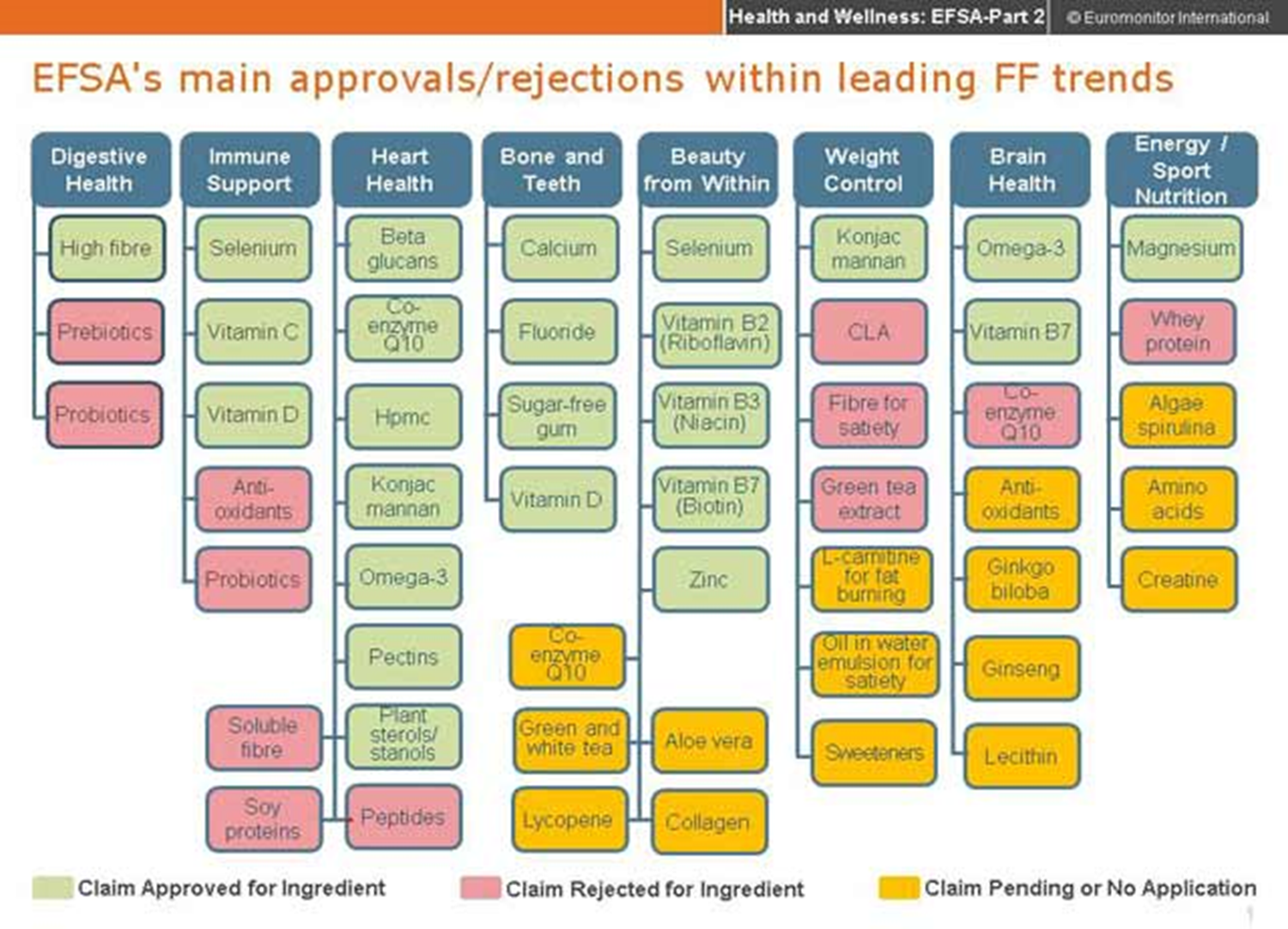
-We face a decrease in the nutritional value of vegetables and fruits as a result of artificial agriculture, climate changes and poor environmental conditions.
-Unfortunately, agricultural products produced in larger quantities in a shorter time with additives are far from providing sufficient vitamin and mineral support. ( Dilution effect ! )
-Modern, scientific, value and quality of food preserving agriculture, harvesting, storage, transportation, processing and food conservation methods can reduce losses.
Brandt, K., & Mølgaard, J. P. (2001). Organic agriculture: does it enhance or reduce the nutritional value of plant foods?. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 81(9), 924-931.
-The study shows that the nutritional values of vegetables rich in magnesium and calcium, such as spinach and broccoli, decrease by almost 50 percent. While 100 g of spinach contained 62 mg of magnesium in the past, today this amount drops to 15 mg. Likewise, 100 grams of broccoli used to contain 100 mg calcium, but now it contains 30 mg calcium.
-Oranges and apples are among the fruits that lose their nutritional value over time. While in the past, 1 orange alone was enough to meet a person's daily need for 400 mg of vitamin C, today it has been determined that the vitamin C content of 1 orange can drop to 4 mg.
Nutritional content of fruit and vegetables
https://www.wasserklinik.com/en/naehrstoffgehalt-von-obst-und-gemuese/
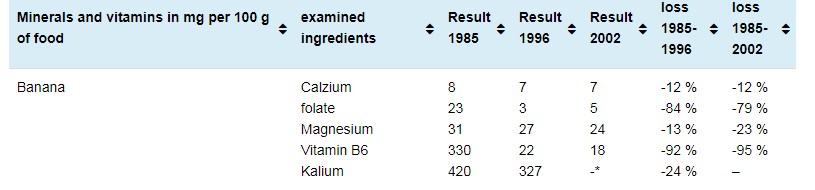
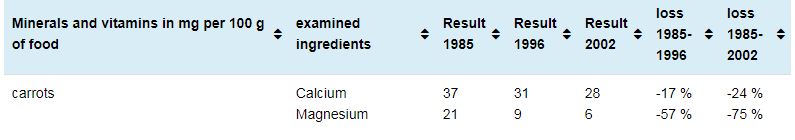



http://www.fao.org/food-loss-reduction/news/detail/en/c/345300/


http://www.fao.org/food-loss-reduction/news/detail/en/c/345300/
“Preventing Vitamin D Deficiency and Maintaining Bone Health Project” has been started by Ministry of Health Maternal and Child Health and Family Planning
With this project, 400 IU vitamin D (10 µg) is intended to be given to babies over a period of 1 year. It has been reported that administration of more than 400 IU of vitamin D for a long should be avoided considering the risks.
- In England, the Ministry of Health recommends 60 mg iron and 2.8 mg folic acid supplements once a week for adolescent girls and women of reproductive age in regions where the prevalence of iron deficiency is 20% or more. (One day a week for 3 weeks, with a 3-week break)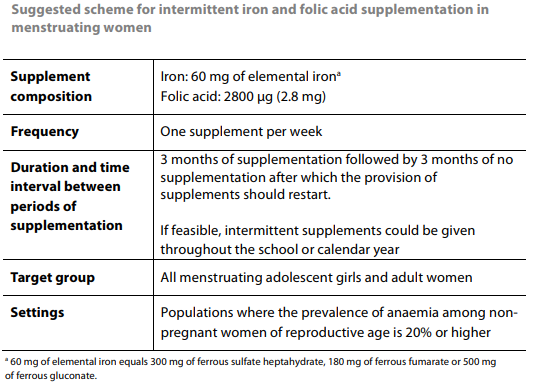
VITAMIN A
-Vitamin A is necessary for vision, growth, reproduction and the immune system.
-Severe Vitamin A deficiency is a cause of death in children, especially due to measles and diarrhea.
-Severe vitamin A deficiency causes xerophthalmia and keratomalacia, which are pathological dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea, resulting in blindness if left untreated.
-One in three preschool children and one in six pregnant women in the world has vitamin A deficiency due to inadequate nutrition. (*World Health Organization)
Retinoid toxicity, Hypervitaminosis A
-Years of intake above 1.5 mg (5000 Units) per day.
-With teratogenic potential (microtia, microgenati, thymic aplasia, facial bone and aortic arch anomalies).
-Early symptoms of chronic hypervitaminosis A appear on the skin dryness and itching
-Anorexia, joint swelling, pain, epiphyseal enlargement growth retardation due to premature closure of eye plaques, internal bleeding,
-Increase in intracranial pressure
-In older age, especially with postmenopausal osteoporosis together with an increased risk of fracture.
Vitamin B1 ( Thiamin )
-Cofactor in glucose metabolism
-Early symptoms of thiamine deficiency are loss of appetite, nausea, and constipation.
-Mental depression, peripheral neuropathy, irritability, fatigue
-Alcohol and Caffeine reduce thiamine absorption
-Nervous system disease due to thiamine deficiency, heart failure due to age beriberi
-Milling both wheat and rice causes significant loss of thiamine. Eating bread made only from white wheat flour causes beriberi cases even in western countries.
-Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome; Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff psychosis. Characterized by encephalopathy, ophthalmoparesis, nystagmus, ataxia and confusion. Other findings of thiamine deficiency such as polyneuropathy, further changes in consciousness (stupor-coma), hypothermia, hypotension may be added to the clinical picture. Korsakoff psychosis is a mental disorder in which memory is significantly affected.
-The risk is especially high in alcoholism and dialysis patients, a situation frequently encountered in hunger strikes.
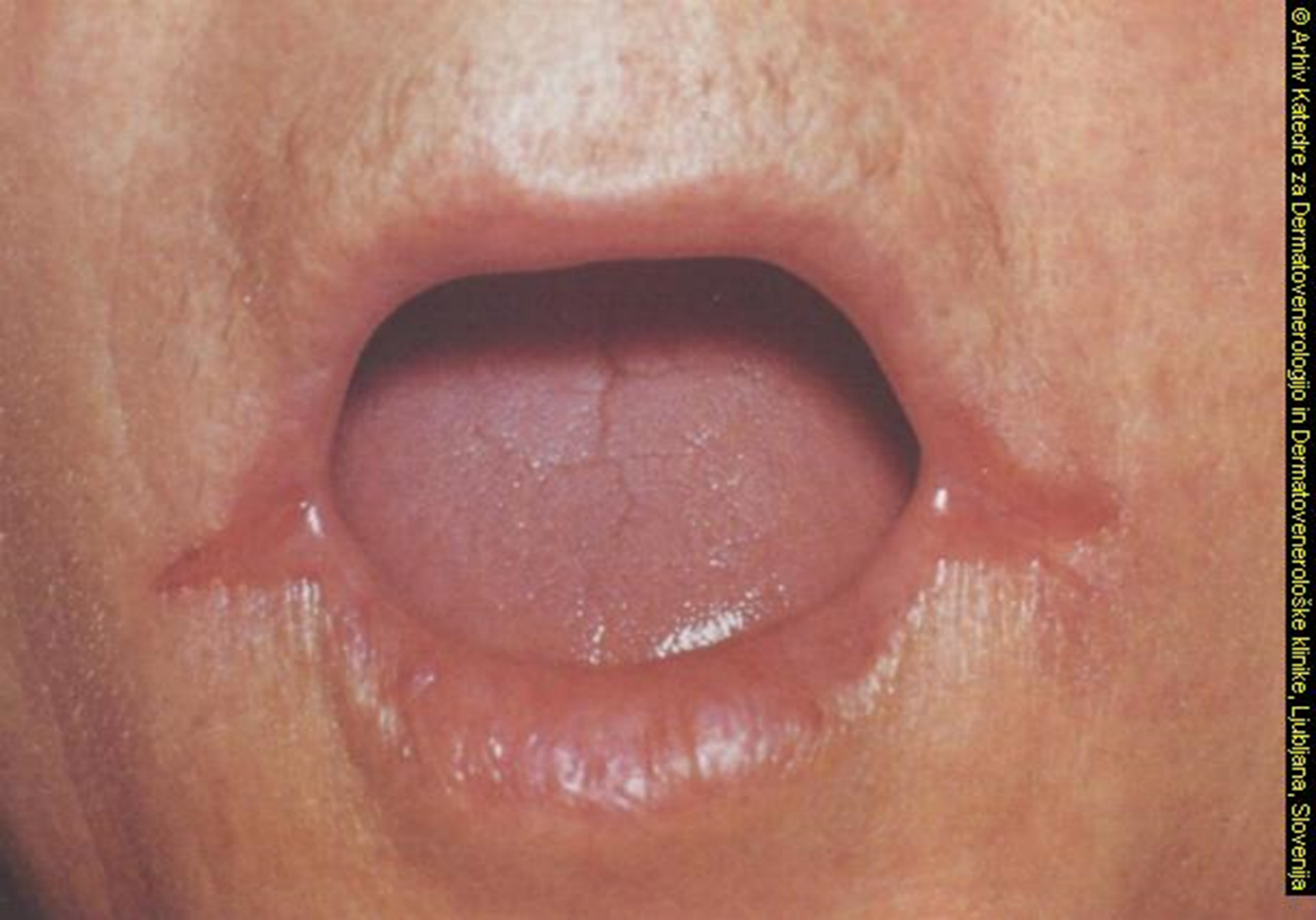
Corner of mouth rages secondary to riboflavin deficiency
Vitamin B3 – Niacin
-Carbohydrate, fat and amino acid metabolism A key building block of many metabolic pathways affecting
-Lowers TG and LDL, increases HDL cholesterol
-Deficiency causes growth retardation, weight loss, anemia
-Pellagra;
-Dermatitis: Symmetrical skin pigmentation on the face, neck and extremities
-Diarrhea: Chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract (stomatitis, glossitis, gastritis)
-Dementia: Central nervous system disorders occur due to degeneration in the nervous tissue.
-Death
Vitamin B5-Pantetonic Acid
-Cofactor in carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism
-It has a role in steroid hormone synthesis
-Necessary for healthy epithelial structure
-Deficiency: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain "Burning food" syndrome due to pantothenic acid deficiency;
-Postural hypotension, tachycardia, epigastric distress, anorexia, and increase in DTR are observed.
-Pantetonic acid deficiency is rare. Because it is widely found in animal and plant foods
Vitamin B6 – Pyridoxine
-Cofactor in carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism
-Vitamin B6 deficiency may develop in the use of alcohol, INH, Theophylline and OKS.
-Deficiency may also occur in babies breastfed by mothers who have developed B6 deficiency due to long-term use of OCS.
-In its deficiency, peripheral neuritis, dermatoses, anemia, muscular dystrophy, cheliosis, glossitis, oxaluria, homocystinuria, bladder stones, hyperglycemia, nausea and vomiting in pregnant women are observed.
-Takes part in the synthesis of serotonin, norepinephrine and sphingolipids
-Glucose tolerance is impaired in the absence of pyridoxine, which is necessary for the stabilization of the glycogen phosphorylase enzyme, which is necessary for glycogen degradation.
-Pyridoxine is also required in the conversion of homocysteine to cysteine and is associated with atherosclerosis due to this reaction.
Neurological symptoms occurring in alcoholism are due to thiamine and pyridoxine deficiency, and hematological problems are due to folate and pyridoxine deficiency.
Low serum concentrations of vitamin B6 and iron are related to panic attack and hyperventilation attack.
Acta Med Okayama. 2013;67(2):99-104.
Mikawa Y, Mizobuchi S, Egi M, Morita K.
Vitamin B7- Biotin
-Cofactor in carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism
-Biotin deficiency does not normally occur because it is widely found in many foods. In addition, most of the biotin requirement is provided by intestinal bacteria.
-Adding raw egg whites to the diet as a protein source causes avidin, a glycoprotein it contains, to bind tightly to biotin and disrupt biotin absorption from the intestine.
-In its deficiency; Dermatitis, glossitis, alopecia, anorexia, nausea, depression, and hallucinations may be observed.
Folic Acid - Vitamin B9
-Folate→THF in growth and cell division It has effects. Especially the intrauterine neural tube is important in development. Neural tube early in fetal life development during the period is critically dependent on the presence of folic acid.
-Daily 400 mg folate use before and during pregnancy, reduces the instances of neural tube defect, cleft palate and Anemia
-The need for folic acid increases during pregnancy and lactation
-Folic acid deficiency may occur in small intestinal absorption pathologies, in alcoholism, anticonvulsant, PPI, oral contraceptive, in methotrexate use, in old age, as a result of consuming vegetables by constantly cooking them
-In folic acid deficiency, the erythroid and myeloid series in the bone marrow are affected. Megaloblastic anemia occurs.
( Hb ↓ MCV ↑ )
-Folic Acid, Vitamin B12 and Pyridoxine (Vit B6) Deficiencies are accompanied by hyperhomocystinemia. (Atherosclerosis!)
Vitamin B12
-Plays a role in hematopoiesis, cell renewal, protein and carbohydrate metabolism
-Use of Antacid, PPI, Metformin, Antibiotics, Aspirin, Gabapentin, Alcohol inhibits the absorption of vitamin B12.
-Intrinsic Factor deficiency in the stomach, atrophic gastritis, H. Pylori inhibits Vitamin B12 absorption
-Absorption is impaired in Total gastrectomy, wide resection of the small intestines in Diphyllobothrium latum infection
-In vitamin B12 deficiency, Myelin sheath synthesis, cell membrane structures are disrupted.
-There is degeneration in the Central nervous system, spinal cord, peripheral nerves.
-Paresthesia, decreased vibration and position sense, Ataxia, decreased DTR, dementia, and psychosis may occur.
-Macrocytic anemia (high MCV), Granulocytopenia, Thrombocytopenia is detected.
Vitamin C

- Vitamin C in elektron microscobe
Vitamin C- Ascorbic Acid
-Vitamin C is a member of a group that includes vitamin E and Beta carotene, known as antioxidants.
-Takes part in collagen formation and tissue repair
-Necessary for mucopolysaccharide synthesis in chondroblast, osteoblasts is
-Plays a role in the synthesis of catecholamines, carnitine and steroid
-It is necessary for iron absorption and ferritin synthesis.
-Deficiency causes immunodeficiency, fatigue, depression and scurvy.
-Scurvy;
-Weakness in connective tissue as a result of deficiency in collagen hydroxylation,
-Delay in wound healing
-bleeding gums
-Bleeding under the skin, in capillaries, ecchymosis
-swelling in joints
-Subperiosteal bleeding, increased risk of fracture
-Anemia
-Smoking increases the need for Vitamin C.
-Aspirin, oral contraceptives and steroids C Reduces vitamin absorption
-Vitamin C reduces the effect of warfarin Vitamin C overdose Can lead to nephrolithiasis and Oxalate nephropathy and
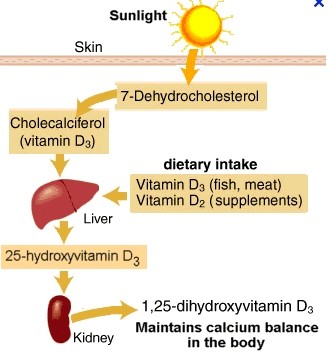 Vitamin D
Vitamin D
-Vitamin D is among the fat-soluble vitamins and is also a group of sterols that are hormones and hormone precursors because they can be synthesized endogenously.
-Its most important effect is on calcium, phosphorus metabolism and bone mineralization.
-Vitamin D plays a regulatory role in apoptosis and cell differentiation.
-Deficiency has been found to be associated with many chronic diseases including infectious and autoimmune diseases like cancer, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome
-Under normal conditions, 90%-95% of the vitamin D needed is synthesized in the skin under the influence of sunlight. Vitamin D taken with food is not of great importance unless specifically added to it .
-To meet our daily needs we need to eat 500 grams of fatty salmon a day and drink 10 glasses of full fat cow's milk. And eggs contain less D3 than milk.
-Using the sun as a source of vitamin D is affected by many factors like climate conditions, ozone density, air pollution, altitude, time of the day and increased skin pigmentation
-Sun protection creams are also known to reduce inhibit the production of vitamin D in the skin significantly.
-While people in high altitude places tend to produce more D3 as they are exposed to sun light more steeply, D3 deficiency is observed more in places with high air pollution.
-D3 is produced in the skin as bond to sulfates thanks to UVB. Sulfate bond is necessary for the storage of D3 and its effects beyond the bone is clear as in sulfate form. That’s why oral D3 intake doesn’t replace the natural D3 intake via sunlight fully.
-To evaluate the vitamin D level, 25(OH)D level whose half-life is 2-3 weeks, which indicates both vitamin D intake and endogenous production, should be checked.
-The adequate Vitamin D intake that is required for bone health and protection against many diseases should be above 30 ng/ml.
Who should have their Vitamin D level checked?
-Children with growth retardation
-Osteoporosis, osteomalacia, pathological fracture
-People with widespread muscle and joint pain
-Those with risk factors of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency
-Those who cannot benefit from enough sunlight,
-Dark-skinned people,
-the elderly,
-obese people,
-Women who get pregnant frequently in short intervals,
-Women in lactation period
-malabsorption,
-Anti-convulsant and Glucocorticoid drug use
-In Chronic Kidney and Liver Failure
Vitamin D in the elderly
-There is evidence that shows the ability to produce vitamin D after UV exposure in the elderly is decreased by four to five percent compared to adults under age of 30.
-There is a significant correlation between the decreases and the levels of 25(OH)D vitamin in the elderly. Vitamin D supplementation can be increased via muscle strength, postural and dynamic balance
-Vitamin D deficiency, especially affects the antigravity muscles of the lower extremities that is required for walking and postural balance and
-Low vitamin levels are found to be associated with poor physical health activity level, decrease in walking speed and balance deterioration
-As a result, vitamin D deficiency in elderly patients is defined as a risk factor for osteoporosis, falls and fractures.
Vitamin D Toxiticy:
-It is the most toxic of all vitamins. Like Other oil-soluble vitamins, vitamin D is stored and metabolized slowly.
-High doses may cause loss of appetite, nausea, thirst and confusion.
-Increased calcium absorption and bone resorption; causing hypercalcemia leads to calcium accumulation in many organs, including arteries and kidneys.
-Risk of vitamin D toxicity has increased in cases such as Granulomatous diseases, genetic diseases, polymorphism of rare enzymes affecting vitamin D metabolism.
Vitamin E – Tocopherols
-Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant in the protection of cell components from free radicals.
-Vitamin E reduces 'LDL' that causes atherosclerosis
-Vitamin E, C and A takes role in avoiding development of cataract.
-In fat digestion disorder, Vit E deficiency appears.
-Anemia may develop due to shortening of the erythrocyte survival period and decrease in hemoglobin production.
-Vitamin supplement should be given during pregnancy, lactation and for the newborn
Vitamin K
-It plays a role in the production of coagulation factors and hemostasis.
-New studies show that vitamin K contributes to healthy bones in the construction, prevention and treatment of osteoporosis .
-Vitamin K deficiency is not observed in a healthy individual, since it can be synthesized by bacteria in the intestine.
-Vitamin K deficiency Usually develops as a result og long-term use of antibiotics, malabsorption, elderly debilitated patients and alcoholism
-Newborns are prone to vitamin K deficiency as they don’t have enough bacteria in their intestines.So to protect against hemorrhagic anemia vitamin K is applied intramuscularly to newborns. However, vitamin K could be given during pregnancy and babies can be given Vitamin K orally after birth.
-Essential Nutrients;
Carbohydrates, Protein, Fats
-Functional foods
-Functional foods of animal origin;
Omega 3 ( α-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ,docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) )
Coenzym Q
Lecithin
Choline
-Phytonutrients : Plant-derived substances that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects;
Flavonoids ( Polyphenols)
Carotenoids ( Lycopene )
Phytoestrogens
Phytoallexin (Resveratrol)
Allyl sulfides
capsaicin
-Vitamin ve Minerals;
Selenium
Copper, Antioxidant enzyme cofactor minerals
Manganeze
Zinc
Funtional Foods
-Activation of detoxifying enzymes is spossible by regulating immune stimulation of the system, cell proliferation and apoptosis related gene expression, hormone metabolism and antibacterial and antiviral effects.